Immigrating to Australia and exploring its ways
Immigration to Australia, the conditions and documents required to immigrate to Australia and in general, obtain permanent residency and Australian citizenship in this paper were examined and analyzed scientifically. But how is it easier for Iranians to immigrate to Australia? What are the requirements for applicants to immigrate to Australia? What are the conditions for investing in this country and migrating to Australia in this way? Is it possible to get a residence permit in Australia by studying in Australia? These are just some of your questions, dear applicants, which are always repeated in conversations with the consultants of Malekpour Law Firm. Therefore, immigration to Australia will be debatable in many ways. In this article, we have tried to be simple and concise. Dear friends, we would like to explain the best points about it to you. Dear friends, you can contact the experts of Malekpour Law Firm (MIE Austria) for additional information about obtaining a residence permit in Australia and benefit from free telephone consultation.
In the comments section, you can ask to see yourself so that they can determine themselves and be able to comment in a timely manner….
Topics covered in this article:
Immigration conditions to Australia
Immigrating to Australia has always been a popular choice for immigration applicants. One of the reasons for migrating to a country is its climatic conditions, the English-speaking people of that country and its strong economy and culture, and most importantly, its immigration potential, so Australia is one of the most fascinated immigrant countries. Applicable is considered among the applicants. However, it is possible to immigrate to Australia in a number of ways, with applicants being able to stay in Australia by any of the above methods. However, you should be aware that due to the growing demand for immigration to Australia, the country has strict conditions. However, there are many people who can immigrate to Australia by providing the necessary conditions. In this article, we will look at several ways to immigrate to Australia so that many applicants can apply according to their circumstances.
Obtaining permanent residence in Australia through work
Immigrating to Australia through work has always been questioned by some immigration applicants. Australian work visas vary widely, depending on the circumstances of all applicants from the Australian Government and Immigration Service, and some of these visas will result in immigration and residency in Australia. Australian work visas will be subject to a special assessment according to the specified class, which is generally measured based on the applicant’s education, individual skills, level of work experience, and ultimately English language proficiency, and is based on Point Based System. If eligible, individuals can enter Australia and obtain a work permit upon receipt of this visa. In this section, we will explain some of the Australian work visas that lead to immigration to Australia.
The process of migrating to Australia through a work visa can be lengthy. Occasionally, people applying for Australian work visas have been found to be frustrated by the time-consuming nature of the process and are reluctant to enter the process as soon as possible, which will accelerate immigration. However, a work visa is the easiest way to immigrate to Australia.
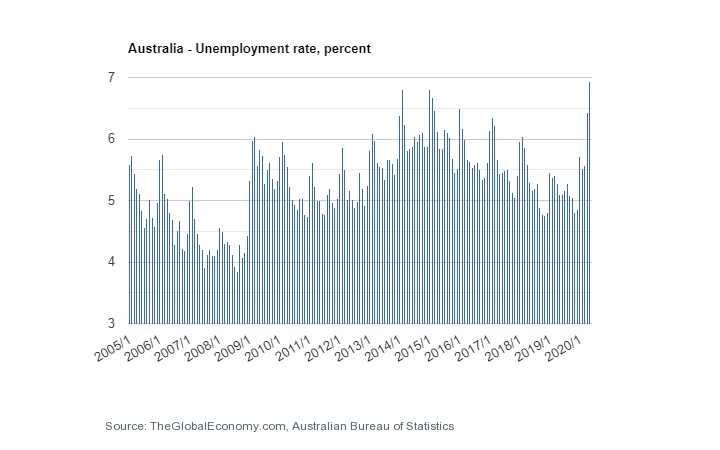
Another important factor for obtaining an Australian work visa is to consider the amount and rate of unemployment in this country, which the following chart can provide you with comprehensive information in this regard.
Conditions for obtaining Australian residency through study
Another way to immigrate to Australia that is of interest to many applicants and has a large following is through study in Australia. According to many people, this method of immigration is very appropriate and logical because people can work in Australia after graduation, by raising the level of their education and with a better understanding of the situation in Australia. To. Of course, one of the strengths of studying in Australia for international job seekers while studying and residing after studying in this country. Regardless of how much international students can cover their expenses during their studies, they can be fully aware of the working conditions and work environment in Australia, which is one of the strengths of studying in Australia. Graduates in Australia can easily enter the job market during their postgraduate residency. Another advantage of immigrating to Australia through study is the lack of restrictions on education. Therefore, students can easily continue their education in schools, colleges and universities. International students can continue their education in more than 1,200 educational institutions in more than 22,000 fields of study.
Tuition fees in Australia are one of the most important factors for applying for an Australian study visa. According to the official website of the Australian government in 2018, tuition fees for international students annually are as follows.
| Grade | Tuition fees |
| Bachelor’s degree | $ 15,000 to $ 33,000 |
| Masters | $ 20,000 to $ 37,000 |
| Ph.D. | $ 14,000 to $ 37,000 |
Of course, international students should keep in mind that tuition fees vary from group to group. For example, studying medicine and paramedical will cost more. Also, study in humanities-related fields is lower than the cost announced in the above category.
Immigrating to Australia through investment
Australia has attracted the attention of many investors around the world due to its high standard of living and ideal economic conditions. Therefore, those interested in migrating to Australia plan to learn more about immigration laws in Australia and the risk of investing in Australia, so that they can immigrate to Australia through investment. That’s why we’re going to look at investment conditions in Australia in this article.
One of the ways to immigrate to Australia by investing in this country is entrepreneurship. Under Australian immigration law, investors, especially entrepreneurs, can start an efficient business that leads to the commercialization of a product or service in Australia and must be able to expand their business in that country.
The Australian Investment Visa is a subset of the 188 Visa and Entrepreneurship Visa in Australia. To obtain this visa, it is necessary to provide the following conditions:
Another type of investment visa in Australia is a Business Talent (Permanent) visa. Applicants can start a new business in Australia through this visa and develop that business. Individuals must consider whether they will be eligible for this visa from the Australian Government and Immigration Service. Applicants must meet the following requirements:
Immigrating to Australia through marriage
Marrying an Australian citizen is another way to immigrate to Australia. However, it should be borne in mind that under Australian immigration law, individuals will not be able to obtain permanent residency by marrying an Australian at the outset. For this reason, they are initially granted a temporary residence permit, which can be extended annually, and they must prove that they have lived with their spouse or partner in Australia for a long time in order to be able to stay in Australia. Submit your application for permanent residence to the Australian Immigration Service. Of course, this statement does not apply to all applicants, as the conditions for applicants and individuals may be quite different. In general, people should consider the following conditions for immigration through marriage:
Immigrating to Australia and obtaining citizenship by birth
All people who intend to immigrate to Australia must comply with the laws and regulations of that country, as in all other countries, and examine its terms and conditions in various ways of obtaining residency and citizenship. The conditions for obtaining citizenship by birth in Australia are not such that children can obtain Australian citizenship as soon as they are born, as obtaining citizenship by birth in Australia includes some of the following:
In general, citizenship by birth in Australia is based on the Right of blood (Jus sanguinis). This means that a child born in this country acquires the citizenship of his or her parents.
Immigrating to Australia through asylum
Immigrating to Australia through Asylum may be done by people who do so without research and without knowing the legal ways to immigrate to Australia, and they are completely unaware of the dangers and financial and human losses.
It should be noted that in 2009, the Australian government approved a humanitarian visa for 12,000 people of this type of visa and immigration program. Of course, it should be noted that this program includes the situation of certain people who are persecuted in their country and discriminated against living conditions and social welfare and all aspects, so that his living conditions are disrupted. His human rights record has been completely violated.
But now the refugee situation in Australia is no longer simple, and the UN High Commissioner for Refugees (UNHCR) is dealing with refugee cases more rigorously.
It is worth mentioning that Malekpour Law Firm has no services or advice in this regard and only remembers the difficult and complicated conditions such as asylum and tries to prevent it by informing about the danger to the lives and property of compatriots.
Immigrating to Australia and the cost of living in Australia
Australia is one of the most developed countries in the world. According to the latest statistics, some of Australia’s most important cities, including Melbourne, have been selected as one of the best cities in the world. This shows the high level of social welfare and the good quality of life of the people in this country, so it can be said that the cost of living in Australia, especially in big cities, is higher. Naturally, many applicants for immigration to Australia tend to be aware of the cost of living in Australia before applying. That’s why we decided to offer you a description of the cost of living in Australia.
| Costs | Items |
| A meal at a cheap restaurant | $ 20 |
| A meal for 2 in a mid-range restaurant | $ 80 |
| Cappuccino | $ 4.37 |
| Coca-Cola / Pepsi 0.33 liter | $ 3.28 |
| 0.33 liters of water | $ 2.72 |
| 1 liter of milk | $ 1.50 |
| 500 grams of bread | $ 2.66 |
| 1 kg of rice | $ 2.61 |
| 12 eggs | $ 4.28 |
| 1 kg of chicken | $ 10.58 |
| 1 kg of red meat | $ 15.95 |
| 1 kg of apples $ | 4.24 |
| 1 kg of bananas | $ 3.46 |
| 1 kg of oranges | $ 3.79 |
| 1 kg of tomatoes | $ 4.97 |
| 1 kg of potatoes | $ 3.30 |
| 1 kg of onions | $ 2.63 |
| Transportation | |
| One way ticket | $ 4.20 |
| monthly ticket | $ 150 |
| 1 km of taxi | $ 2 |
| 1 liter of gasoline | $ 1.47 |
| Applications on a monthly basis | |
| Water, electricity, gas, internet and 8 for an 85-meter apartment | $ 203.83 |
| Apartment for rent per month | |
| 1 bedroom apartment in downtown | $ 1656.75 |
| 1 bedroom apartment outside downtown | $ 1270.15 |
| 3 bedroom apartment in downtown | $ 2658.21 |
| 3 bedroom apartment outside downtown | 1877.29 dollars |
*This data is based on the latest update in December 2019.
*Costs are based on the Australian dollar.
Immigrating to Australia and obtaining Australian citizenship
As mentioned in this article, immigration to Australia and obtaining Australian residency are possible in six different ways (employment, education, investment, birth, asylum, and marriage), which we have examined. This article was written by Malekpour Law Firm and any copying of it is considered unauthorized and unprofessional. To better understand this issue, you can see the conditions for obtaining citizenship in Australia in several ways.
Answer common questions about immigration to Australia
✅Where do I start to immigrate to Australia?
The first step to immigrating to Australia is to learn how to immigrate to Australia and choose the best option. Then you have to provide the conditions and documents of immigration based on the chosen method.
✅What are the best ways to immigrate to Australia?
Studying in Australia, permanent residency through the Skilled Worker program, investment programs and entrepreneurship programs are some of the best ways to immigrate to Australia.
✅Can I immigrate to Australia without an immigration lawyer?
Yes. You can read the legal immigration information on Australia’s official website, but a lawyer can do your job more quickly and share experiences that are not covered by official law.
✅How much does it cost to live in Australia?
The average cost of living in Australia per month is $ 3,000 per person and $ 6,000 for a family of four.


Leave a Reply
Want to join the discussion?Feel free to contribute!